From a simple team request to a data collection app!
Even the smallest operational tasks present an opportunity for innovation. When our team needed a quick way to collect food and drink preferences for an upcoming social event, I saw more than just a logistical challenge, I saw a chance to demonstrate the power of low-code solutions in action.
Instead of flooding everyone’s inbox with emails and chasing down responses, I saw an opportunity to create something more engaging and efficient. As a data consultant, I couldn’t resist the chance to build a custom application. What started as an administrative task quickly turned into a an application built in Power Apps—no heavy coding, no complicated tools, just pure Power Apps magic—delivered with zero code, in record time.
The challenge: gather staff preferences, but make it easy
The task seemed simple: collect food, drink, and dietary preferences from the team for an event. But the real challenge was to:
- Avoid messy email chains
- Eliminate manual tracking of responses
- Bypass clunky spreadsheets
It had to be quick, easy, and, of course, a little fun.
The solution: a no-code approach with Power Apps
Step 1: Create the app
Power Apps is a collection of low-code tools that allows you to build custom applications—usually for business purposes, but also to build automation pipelines, and analyse data. To build the app, I followed three simple steps:

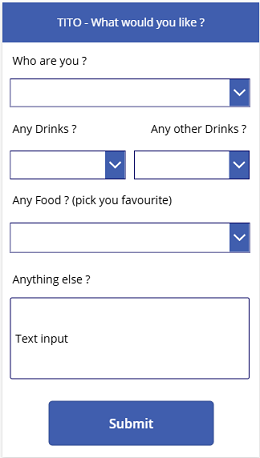
- Building the form: I created a straightforward form where colleagues could choose from options like vegetarian, gluten-free, vegan, coffee, tea, etc… With Power Apps’ drag-and-drop functionality, I had an efficient, interactive form up and running in no time. It is very simple, yet effective.
- Keeping it clean with data validation: No one wants to deal with messy inconsistent data. I added validation rules to ensure accurate inputs, preventing duplicates and incomplete responses.
- Automating the logging of data: Instead of manually compiling responses, I set up Power Automate to instantly log submissions into an Excel file. With each form submission, data was captured, stored, and ready for review—no manual work required.
For simplicity, I connected my app to an Excel file. While you can create a data-driven application that does not rely on a database, the real value lies in connecting it to pre-existing data on a database. However, for this scenario, we continued without a database link.
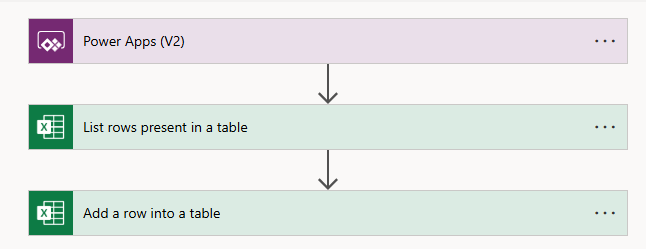
Step 2: Raw, high-quality data
With the App shared with the team, all responses were available immediately in the linked Excel file. Due to our structured way of collecting responses, matched with our validation processes, we were guaranteed high quality data. No clean up tasks, or feedback loops with respondents, just high-quality structured data.
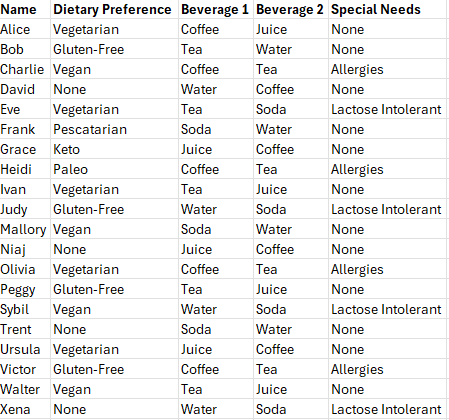
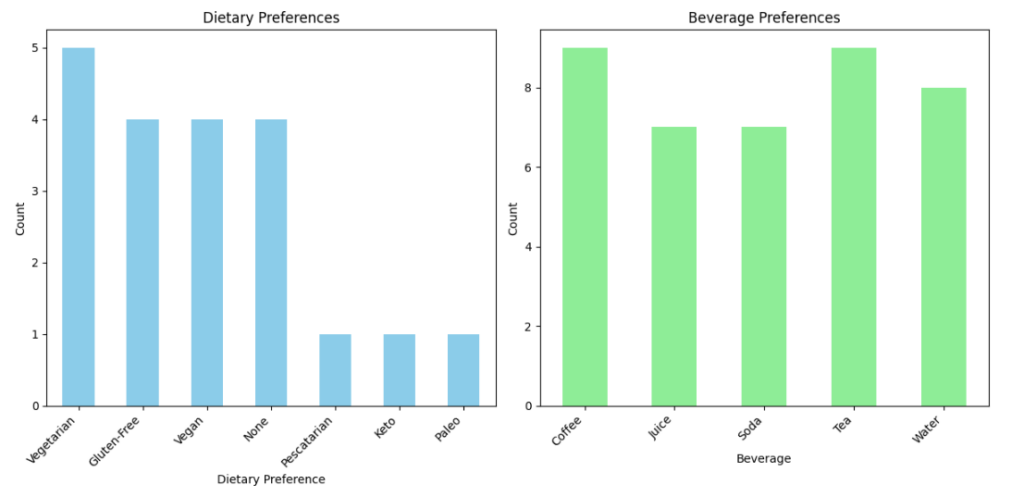
Step 3: The outcome—data collected; event sorted!
With clean data comes insights and reports that can be trusted. I used the responses from the App to build a shopping list that provided refreshments for everyone throughout the social event – no one left hungry.
Beyond Power Apps: The bigger picture of data applications
While Power Apps was the perfect no-code tool for this quick-win scenario, businesses with more complex data needs might require additional flexibility, customisation, and scalability. That’s where other data application frameworks come into play:
- Streamlit – Great for building lightweight, Python-powered data applications with interactive dashboards.
- Streamsync (Writer) – A newer alternative designed for real-time, collaborative data apps.
- Custom Python Applications – Ideal for full-scale automation, data transformation, and deeper integrations with company databases.
Each tool offers unique strengths depending on your use case—from simple form-based data collection to enterprise-grade predictive analytics.
The real value of custom data applications:
Data applications help to make simple data collection processes more efficient than Excel or Email-driven processes. However, they can offer many more benefits, which may include:
1. Centralised source of truth
• Data application: All users work with the same real-time data stored in a central database.
• Email/Excel: Prone to version control issues; multiple file versions can cause confusion and errors.
2. Real-time access & updates
• Data application: Live updates mean users always see the most current data.
• Email/Excel: Manual sending and versioning delays updates and increases the risk of outdated information being used.
3. Better data integrity & validation
• Data application: Built-in validation rules prevent incorrect or incomplete entries.
• Email/Excel: Easy to enter wrong data or overwrite formulas accidentally.
4. Improved collaboration
• Data application: Multiple users can interact with the system simultaneously with proper access controls.
• Email/Excel: Collaboration is clunky—usually involves back-and-forth emails and conflicting edits.
5. Enhanced reporting & insights
• Data application: Can integrate dashboards, visualizations, and advanced analytics.
• Email/Excel: Reporting is static and must be manually created and updated.
6. Integration with other systems
• Data application: Easily connects with APIs, databases, and third-party tools (e.g., CRMs, ERPs, BI tools).
• Email/Excel: Limited integration; often requires manual data export/import.
7. Access control & security
• Data application: Role-based access ensures sensitive data is only visible to authorised users.
• Email/Excel: Risky—spreadsheets can be emailed or forwarded without restrictions.
8. Scalability
• Data application: Designed to handle growing data volumes and user needs.
• Email/Excel: Becomes slow and unwieldy as data grows or processes get more complex.
9. Automation
• Data application: Automates repetitive tasks like notifications, calculations, and workflow steps.
• Email/Excel: Requires manual effort for most processes.
10. Auditability & tracking
• Data application: Can log changes and track user actions for audit/compliance.
• Email/Excel: Hard to trace changes and understand the history of data modifications.
What’s next?
This is just one small example of how a simple request can be turned into an automated, interactive data solution. In our upcoming blog series, we’ll explore:
- When to use low-code vs. custom-built data applications
- How businesses can integrate data apps with enterprise data systems
- A comparison of Power Apps, Streamlit, Streamsync (Writer), and Python-based solutions
Stay tuned!
Escape the manual data processes in your operational reporting and data collection workflows today!
Get in touch to see how we can help you build smarter, automated, enterprise-grade data applications, or learn more about our data application solutions.

